バイオテクノロジーの進歩は、一昔前なら夢物語でしかなかったことを現実にしてくれます。動物の脳の活動をリアルタイムで見せてくれるGCaMPも、そんなテクノロジーのうちのひとつ。GCaMPという名前を聞くのは初めてという人でもGFP (Green Fluorescent Protein)ならどこかで聞いたことがあるのではないでしょうか?GFPは、下村脩博士がオワンクラゲから見つけたもので、タンパク質なのに緑色の蛍光を発するという画期的な性質を持つものです。この研究で下村博士は2008年にノーベル化学賞を受賞しており、GFPは高校の生物の教科書にも紹介されています。このGFPを人工的に改造して、カルシウムイオンが結合するとより明るく光るようしたタンパク質がGCaMPです。つまりGCaMP蛍光強度の変化が、カルシウムイオン濃度の変化に対応するわけです。
目次
GCaMPって誰がいつ発明したの?
2001年に中井淳一博士らのグループにより発明されました(Nakai et al., Nat Biotechnology 2001)。
我々が開発したG-CaMPはGFP1分子とカルモジュリンとミオシン軽鎖キナーゼのM13断片からなる一波長励起一波長測光タイプの蛍光カルシウムプローブである。GFPと同様のスペクトル特性を持っているので標準的な蛍光顕微鏡やレーザー顕微鏡で容易に観察することができる。G-CaMPの最大の特徴はG-CaMPが蛋白質であるためG-CaMPをコードする遺伝子をプロモーターの制御下に発現させることで,簡単に細胞特異的なプローブの導入ができる点である。(GFPを用いた蛍光カルシウムプローブG-CaMPの開発 中井淳一・大倉正道 比較生理生化学Vol.19,No.2(2002))
GCaMPはカルシウムセンサーとして機能し、カルシウムイオン濃度が高いほど明るい蛍光を発してくれますので、神経細胞に限らず、どんな種類の細胞であれ、細胞内にG-CaMPを導入してやるとその細胞のカルシウムイオン濃度の変化を、G-CaMPの蛍光強度変化として捉えることができます。
GCaMPって何の略?
2001年の原著論文では、green fluorescent protein (GFP)-based Ca2+ probesとしか書いていませんが、
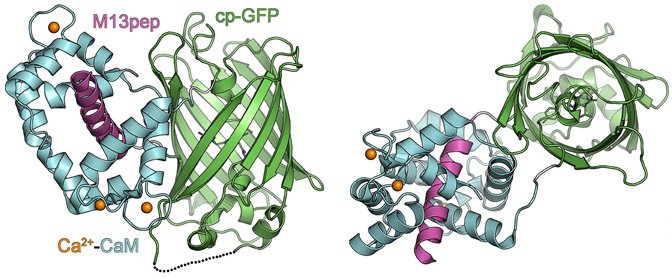 (GCaMPタンパク質の立体構造。左側は横から見た図で、右側は縦方向から見た図。Akerboom et al., 2013 Fig.3を改変)
(GCaMPタンパク質の立体構造。左側は横から見た図で、右側は縦方向から見た図。Akerboom et al., 2013 Fig.3を改変)
カルモジュリン(Calmodulin)はCaMと表記されますので、GはGFPのG,CaMはカルモジュリンのCaM、PはProteinのPでしょうか。
Green fluorescent protein – calmodulin protein – (GCaMP)-type GECI are based on a circularly permutated EGFP molecule (cpEGFP) flanked at the N and C termini by the smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase derived calmodulin binding peptide (RS20) and calmodulin (CaM), respectively. (Helassa et al., Scientific Reports volume 5, Article number: 15978 (2015))
In our laboratory, we have focused our efforts to improve genetically encoded calcium indicator proteins (GECIs), specifically the green fluorescent protein (GFP)-Calmodulin fusion protein (GCaMP).(Badura et al., 2014 doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.1.2.025008)
G-CaMPそれともGCaMP?
2つの単語をハイフンでつないで1語にしていたものが、一般的になるにつれてハイフンがとれて完全な一語になるということが起こります。G-CaMPもそうやってGCaMPになったのかと思いきや、どうやらそう単純ではないようです。発明者である中井博士らのグループは今日に至るまでG-CaMPと表記しており、G-CaMPの改良型を作製し発表した他のグループはGCaMPと表記しています。あまり気にしていない論文も見受けられます。特定のGCaMPについて言及する際には、そのGCaMPを報告した論文内でどう表記されているかに気を配る必要があるでしょう。
Here we report the development of a high-affinity Ca(2+) probe composed of a single GFP (named G-CaMP). (Nakai et al., Nat Biotechnol. 2001 Feb;19(2):137-41.)
Generation and Imaging of Transgenic Mice that Express G-CaMP7 under a Tetracycline Response Element. (Sato et al., 2015 PLoS One 10(5):e0125354)
歴史的にも多少ややこしいことになっています。G-CaMPの改良型を報告した2006年の論文には中井博士らも共著者として入っていますが、ここではGCaMP2と命名されており、オリジナルのG-CaMPのことをGCaMP1としています。
Designed and random alterations in the previously described, circularly permutated eGFP-based, Ca2+-sensing molecule, which we now term GCaMP1 (11), were undertaken to improve brightness and stability. (Imaging cellular signals in the heart in vivo: Cardiac expression of the high-signal Ca2+ indicator GCaMP2. Yvonne N. Tallini, Masamichi Ohkura, Bum-Rak Choi, Guangju Ji, Keiji Imoto, Robert Doran, Jane Lee, Patricia Plan, Jason Wilson, Hong-Bo Xin, Atsushi Sanbe, James Gulick, John Mathai, Jeffrey Robbins, Guy Salama, Junichi Nakai, and Michael I. Kotlikoff. PNAS March 21, 2006. 103 (12) 4753-4758)
Howard Hughes Medical Institute/Janelia Research Campusの研究者らはGCaMPとハイフンを入れない表記をしています。
Imaging neural activity in worms, flies and mice with improved GCaMP calcium indicators. Tian L, Hires SA, Mao T, Huber D, Chiappe ME, Chalasani SH, Petreanu L, Akerboom J, McKinney SA, Schreiter ER, Bargmann CI, Jayaraman V, Svoboda K, Looger LL. Nat Methods. 2009 Dec;6(12):875-81.
そんなわけで、G-CaMPとGCaMPの両方の表記が世の中で見られます。
GCaMPで何が見えるの?
細胞の中に導入されたGCaMPは、細胞内カルシウムイオン濃度をモニターして可視化してくれますので、カルシウムイオンの濃度変化が生じるような生命現象なら何でも可視化することができます。そのような生命現象としては受精、細胞分裂、細胞の分化、細胞の移動、筋収縮、神経細胞の興奮などいろいろあります。
下の動画はショウジョウバエの排卵のときに卵母細胞内のカルシウム濃度が上昇する様子(排卵時のカルシウム動態は14秒あたりから)。
PNAS : Calcium waves occur as Drosophila oocytes activate
(In vivo imaging at dissection scope resolution of Ca2+ flux in activating oocytes from transgenic flies expressing GCaMP3 in their oocytes. See text and the legend to Fig. 1A for details. 論文 https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1420589112)
下の動画は、線虫(C. elegans)という小さな小さなミミズみたいな生き物が動いている様子ですが、筋肉の細胞にGCaMPが導入されているため、筋収縮が起きているところが明るく光ります(擬似カラー表示されていて、暖色系の明るい色がカルシウム濃度の高い部分)。体が屈曲しているときに曲がりの内側部分のほうが明るくなる、つまり筋肉が収縮していることがわかります。
Ca2+ dynamics in body wall muscles of wild-type C. elegans
(Genetic crosses were made to transfer the genetically encoded Ca2+ indicator GCaMP3.35 (Schwarz et al., 2011) into the vps-36 (gk427) background. 論文リンク http://jcs.biologists.org/content/129/7/1490)
下の動画の実験では、視覚を司る脳部位の神経細胞にGCaMPが導入されており、熱帯魚の一種ゼブラフィッシュ(ペットショップでの名前はゼブラダニオ)の稚魚が餌となるゾウリムシを見ているときに脳が活動している様子を見せてくれます。
Neuronal Activity during Visual Perception 脳に映る視覚世界をリアルタイムで観察
(The gSA2AzGFF49A;UAS:GCaMP7a double-transgenic zebrafish used for imaging were also homozygous for the nacre pigmentation mutation [24] to eliminate melanophores. 論文リンク https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.12.040)
下の画像は新世界ザルの一種コモン・マーモセットが左手や左足を触られたときの脳(右側の体性感覚野)の活動の様子。動画は画像をクリックしてリンク先でご覧ください。
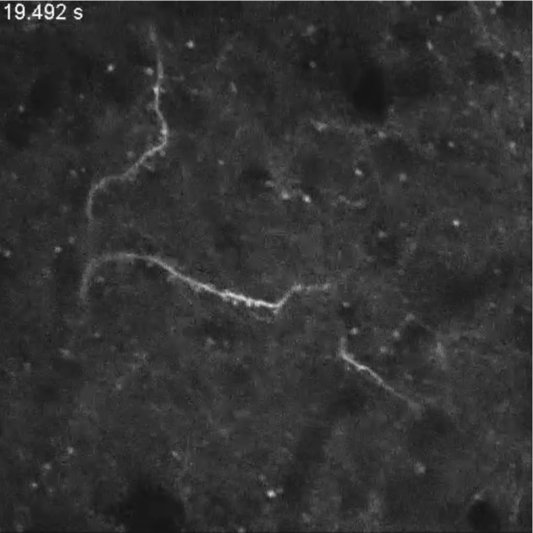
(Here, we report a method for long-term imaging of a GECI, GCaMP6f, expressed from adeno-associated virus vectors in cortical neurons of the adult common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus), a small New World primate. 論文リンク https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.10.050)
GCaMPってどれがいいの?
研究者がこれからカルシウムイメージングをしてみたいという場合には、どのカルシウムプローブを選ぶかは重大な決断となります。G-CaMP(GCaMP)の場合、2001年の最初の報告以来、改良に改良が重ねられてきて、しかも発明者らを含む複数のラボが独立して改良に取り組んだため、改良型GCaMPの名前が必ずしも統一的になっておらず、かなり混乱させられる状況です。同じラボで開発されたものであればバージョンの数字が大きいほど一般的に性能が良い(シグナルノイズ比が良い、微弱なカルシウムイオン濃度の変化を検出可能)と言えるのでしょう。ただし理屈を言えば、見たい生理現象で変化するカルシウムイオン濃度の範囲がどのあたりかに合わせて、その範囲でシグナル強度がもっとも大きく変化するような解離定数を持つGCaMPを選ぶ必要があります。また、カルシウムシグナルの時間変化が速い現象を高い時間分解能で検出したいのであれば、GCaMPとカルシウムイオンが一度結合したあとに速やかに離れるようなものを選ぶ必要があります。シグナル(蛍光強度変化)を大きくするために、低カルシウム濃度における蛍光強度を弱く抑えた設計になっているものでは、カルシウムイオンが増加しない限り細胞がGCaMPの蛍光では見えにくく、実際には使いづらいという状況も有り得ます。結局のところ、どのGCaMPがベストかは、見たい生命現象、実験目的、実験のデザインによって変わってくると言えそうです。
jGCaMP7シリーズ (ジャネリア・ファーム)
ジャネリア・ファームの研究グループが新たにjGCaMP7のシリーズを開発し、論文発表前ですが既に塩基配列を公開しています。
(引用元:https://www.janelia.org/project-team/genie)
追記:論文のプレプリントが2018年10月3日にbioRxiveに投稿されていました。
High-performance GFP-based calcium indicators for imaging activity in neuronal populations and microcompartments.
GCaMP6シリーズ (GCaMP6s, GCaMP6f, GCaMP6m) (ジャネリア・ファーム)
個々のGCaMP6の名前の最後に付いているアルファベットs, f, mは、キネティクスの速さがそれぞれスロー、ファースト、メディウムであることを示しています。
Using structure-based mutagenesis and neuron-based screening, we developed a family of ultrasensitive protein calcium sensors (GCaMP6) that outperformed other sensors in cultured neurons and in zebrafish, flies and mice in vivo.
Based on screening in cultured neurons (Fig. 1), we chose three ultrasensitive GCaMP6 sensors (GCaMP6s, 6m, 6f; for slow, medium and fast kinetics, respectively) for characterization in vivo. These sensors vary in kinetics, with the more sensitive sensors having slower kinetics. (Chen et al., 2013 Nature 499, 295-300)
G-CaMP6, G-CaMP7, G-CaMP8およびそのヴァリアント (中井博士らのグループ)
The dynamic range of G-CaMP7 (Fmax/Fmin = 36.6±4.10, n = 3) was ∼3-fold greater than that of G-CaMP6, even though this variant showed a lower Ca2+ affinity (Kd = 243±14 nM, n = 3) than G-CaMP6 (Fig. 1B and C). By performing further random mutagenesis on G-CaMP7, we obtained a more sensitive variant of G-CaMP7 termed G-CaMP8, (Ohkura et al., 2012 PLOS ONE https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051286)
we introduced amino acid substitutions into GCaMP-HS, tested their activities, and developed a new version, which we named GCaMP7a (Muto, Ohkura et al., 2013. Curr Biol. 23(4):307-311)
Caプローブのさらなる改良
- 脳情報動態の多色HiFi記録を実現する超高感度カルシウムセンサーXCaMPを開発-東大 (2019年05月14日 PM12:00 医療NEWS)従来のGECIはHill係数が2~3付近であることから、複数の発火に対し非線形的に蛍光強度が変化し、かつ、広範囲のCa2+濃度を検出するのが困難だった。そこで研究グループは、これらの問題を解決するために、超高速、高感度、Hill係数1かつダイナミックレンジが大きい多色GECIを作成することを目指した。
Calcium Imaging Gets a Multicolor Makeover / Cell, May 9, 2019 (Vol. 177, Issue 5) 2019/05/10 Cell Press
参考
ブログ
- GCaMP7(A317Lとは?) jGCaMP7 cultured neuron data (Mのメモ 2018-02-14)
参考論文(【開発元とGCaMPのバージョン】)
- 【ジャネリア jGCaMP7シリーズ】jGCaMP7 (addgene.com) (論文未発表)
- 【ジャネリア GCaMP6シリーズ】Ultrasensitive fluorescent proteins for imaging neuronal activity. Chen et al.,2013. Nature 499:295–300. “we developed a family of ultrasensitive protein calcium sensors (GCaMP6) that outperformed other sensors in cultured neurons and in zebrafish, flies and mice in vivo.” “Based on screening in cultured neurons (Fig. 1), we chose three ultrasensitive GCaMP6 sensors (GCaMP6s, 6m, 6f; for slow, medium and fast kinetics, respectively) for characterization in vivo.”
- 【中井博士ら GCaMP7a】Real-Time Visualization of Neuronal Activity during Perception. Muto, Ohkura et al., 2013.Curr Biol. 23(4):307-311. “we introduced amino acid substitutions into GCaMP-HS, tested their activities, and developed a new version, which we named GCaMP7a”
- 【中井博士ら G-CaMP6, G-CaMP7, G-CaMP8】Genetically Encoded Green Fluorescent Ca2+ Indicators with Improved Detectability for Neuronal Ca2+ Signals. Ohkura et al., 2012. PLOS ONE 7(12): e51286. “As expected, G-CaMP6, a variant of G-CaMP5.09 bearing an M36L substitution in the CaM domain (Fig. 1A), showed a higher Ca2+ affinity (Kd = 158±4.0 nM, n = 3) than G-CaMP5.09 or the previously reported G-CaMP2 variants G-CaMP-HS [17] and G-CaMP3 [4] (Fig. 1B and C).” ” Next we performed random mutagenesis on G-CaMP6 by using an error-prone PCR [15] and were able to screen a highly responsive variant termed G-CaMP7, which differs from G-CaMP6 by a deletion of histidine (ΔH) in the RSET domain and an S205N mutation in the circularly permutated EGFP domain (Fig. 1A). The dynamic range of G-CaMP7 (Fmax/Fmin = 36.6±4.10, n = 3) was ∼3-fold greater than that of G-CaMP6, even though this variant showed a lower Ca2+ affinity (Kd = 243±14 nM, n = 3) than G-CaMP6 (Fig. 1B and C). By performing further random mutagenesis on G-CaMP7, we obtained a more sensitive variant of G-CaMP7 termed G-CaMP8,”
- 【ジャネリア GCaMP5シリーズ】Optimization of a GCaMP Calcium Indicator for Neural Activity Imaging. Akerboom et al., 2012.J Neurosci 32 (40) 13819-13840 “Through protein structure determination, targeted mutagenesis, high-throughput screening, and a battery of in vitro assays, we have increased the dynamic range of GCaMP3 by severalfold, creating a family of “GCaMP5” sensors.” “Consequently, the Asp380Tyr mutation raises the brightness of the calcium-bound state of GCaMP3 for both GCaMP5A and GCaMP5G; in addition, calcium affinity and cooperativity (Hill coefficient) are increased by ∼25% for GCaMP5A (Table 1).”
- 【中井博士ら G-CaMP 4.1】Tissue-Tissue Interaction-Triggered Calcium Elevation Is Required for Cell Polarization during Xenopus Gastrulation. Shindo et al., 2010. PLoS ONE 5(2): e8897. “G-CaMP 4.1, which is an improved form of a previously reported calcium indicator,”
- 【中井博士ら GCaMP-HS】Genetic visualization with an improved GCaMP calcium indicator reveals spatiotemporal activation of the spinal motor neurons in zebrafish. Muto, Ohkura et al., 2011. PNAS 108 (13) 5425-5430. “we developed GCaMP-HS (GCaMP-hyper sensitive), an improved version of the genetically encoded calcium indicator GCaMP,” “Kd and Hill coefficient of GCaMP-HS were 102 nM and 5.0, respectively (Fig. 1D). Kd and Hill coefficient of GCaMP2 were 146 nM and 3.8, respectively, indicating that GCaMP-HS has a higher affinity to Ca2+ ions and a higher cooperativity”
- 【ジャネリア GCaMP3】Imaging neural activity in worms, flies and mice with improved GCaMP calcium indicators. Tian et al., 2009. Nat Methods. 6(12):875-81.”We developed a single-wavelength GCaMP2-based GECI (GCaMP3), with increased baseline fluorescence (3-fold), increased dynamic range (3-fold) and higher affinity for calcium (1.3-fold). We detected GCaMP3 fluorescence changes triggered by single action potentials”
- 【ジャネリア GCaMP2結晶構造解析】Crystal Structures of the GCaMP Calcium Sensor Reveal the Mechanism of Fluorescence Signal Change and Aid Rational Design. Akerboom et al., 2009. J Biol Chem. 284, 6455-6464
- 【ジャネリア&中井博士ら GCaMP2】Imaging cellular signals in the heart in vivo: Cardiac expression of the high-signal Ca2+ indicator GCaMP2.
Tallini, Ohkura, et al., 2006. PNAS 103 (12) 4753-4758. “previously described sensors have proved to be of limited use to report cell signaling in vivo in mammals. Here, we describe an improved Ca2+ sensor, GCaMP2,” - 【中井博士ら 元祖G-CaMP】A high signal-to-noise Ca2+ probe composed of a single green fluorescent protein. Nakai et al., 2001. Nat Biotech. 19:137–141.